Difference between revisions of "Overview"
Gcronkright (talk | contribs) (→What can I do with the ADF?) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
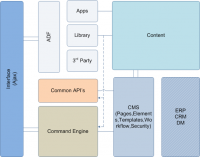
| − | The Application Development Framework (ADF) | + | The Application Development Framework (ADF) is an open source framework that essentially sits on top of (or next to) your CommonSpot installation. The ADF is a combination of Server and Site level object factories built using the open source Lightwire Object Factory (visit the [[Glossary|Term Glossary]] for definitions of the terminology used with the lightwire object factory) |
| − | + | The framework consists of essentially these major components: | |
| + | * [[ADF Applications|Applications]] (Apps) - Custom built applications that can be a combination of components (cfc's), custom coding (custom field types, custom scripts, renderhandlers etc...) and common ADF library components | ||
| + | * [[Lib|Library]] - Organized components designed to extend your CommonSpot development by giving you simple access to data within CommonSpot (like pages, subsites, documents, images and custom elements) | ||
| + | * [[Extensions|Extensions]] - Global custom scripts, custom field types, datasheet modules, render handlers, etc... Extensions can be imported into you current CommonSpot sites to achieve enhanced functionality. | ||
| + | * [[ThirdParty|ThirdParty]] - Third party software used to enhance the interface or interaction with CommonSpot data. Examples include, jQuery plugins, jQuery UI, swfobject etc... | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:CommonSpot_Stack_2010.png|thumb|200px|none|alt=CommonSpot 6.0 Stack w/ the ADF.|CommonSpot 6.0 Stack w/ the ADF]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == What can I do with the ADF? == |
| − | + | At the simplest level you can use the ADF to access content within your CommonSpot installation programattically. For instance if you had a custom element named "News" and you wanted to get all of the content/records for that custom element you could use the ADF and write code like this: | |
| − | == ADF | + | <!-- <source lang="cfm"> --> |
| − | + | <cfset myData = application.ADF.ceData.getCEdata("News")> | |
| + | <!-- </source> --> | ||
| − | + | What you choose to do with that data is completely up to you. Prior to the ADF, the only way you could access the data like this would be to write your own code against the CommonSpot database. | |
| − | + | The above example is only the beginning. The ADF is so much more. With the ADF you can also do some of the following: | |
| − | * | + | * Access Standard and Custom Metadata for any page and/or document in CommonSpot: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <cfset metadata = application.ADF.csData.getStandardMetadata(pageID)> | ||
| + | <cfset customdata = application.ADF.csData.getCustomMetadata(pageID)> | ||
| − | + | * Access common tools typically found on the cflib.org site: | |
| − | + | <cfset myArray = application.ADF.data.queryToArrayOfStructures(myQuery)> | |
| − | + | * Connect two CommonSpot elements together using the new [[General Chooser]] and [[Custom Element Select]] custom field types | |
| − | * [[Custom | + | * Download applications built using the ADF and add features to your site like [[Profiles]], [[Forums]], [[Blogs]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * Build [[ADF Applications| Applications]] using the ADF to distribute amongst your CommonSpot sites or share with the Community |
| − | * [[ | + | * Add [[ADF lightbox| lightbox]] interfaces to any of your applications/custom field types using code like: |
| − | * [[ | ||
| − | == | + | <cfset application.ADF.scripts.loadADFLightbox()> |
| − | + | <div rel="myCustomScript.cfm" class="ADFLightbox">Open in lightbox</div> | |
| − | = | + | Body of the myCustomScript.cfm file being opened in the lightbox |
| − | + | <cfset application.ADF.scripts.loadADFLightbox()> | |
| + | <cfset application.ADF.ui.lightboxHeader(lbTitle="myCustomScript")> | ||
| + | <cfoutput>{Lightbox Page Content}</cfoutput> | ||
| + | <cfset application.ADF.ui.lightboxFooter()> | ||
| − | + | == Getting Started == | |
| − | + | The best way to get started using the ADF is to [[ADF Installation|Install]] it. | |
| − | + | Once you have the ADF installed you can: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Browse the [http://community.paperthin.com/projects/browse.cfm applications] available on the Community Site | |
| − | * [ | ||
[[Category:Landing Page]] | [[Category:Landing Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:48, 1 May 2014
Overview
The Application Development Framework (ADF) is an open source framework that essentially sits on top of (or next to) your CommonSpot installation. The ADF is a combination of Server and Site level object factories built using the open source Lightwire Object Factory (visit the Term Glossary for definitions of the terminology used with the lightwire object factory)
The framework consists of essentially these major components:
- Applications (Apps) - Custom built applications that can be a combination of components (cfc's), custom coding (custom field types, custom scripts, renderhandlers etc...) and common ADF library components
- Library - Organized components designed to extend your CommonSpot development by giving you simple access to data within CommonSpot (like pages, subsites, documents, images and custom elements)
- Extensions - Global custom scripts, custom field types, datasheet modules, render handlers, etc... Extensions can be imported into you current CommonSpot sites to achieve enhanced functionality.
- ThirdParty - Third party software used to enhance the interface or interaction with CommonSpot data. Examples include, jQuery plugins, jQuery UI, swfobject etc...
What can I do with the ADF?
At the simplest level you can use the ADF to access content within your CommonSpot installation programattically. For instance if you had a custom element named "News" and you wanted to get all of the content/records for that custom element you could use the ADF and write code like this:
<cfset myData = application.ADF.ceData.getCEdata("News")>
What you choose to do with that data is completely up to you. Prior to the ADF, the only way you could access the data like this would be to write your own code against the CommonSpot database.
The above example is only the beginning. The ADF is so much more. With the ADF you can also do some of the following:
- Access Standard and Custom Metadata for any page and/or document in CommonSpot:
<cfset metadata = application.ADF.csData.getStandardMetadata(pageID)> <cfset customdata = application.ADF.csData.getCustomMetadata(pageID)>
- Access common tools typically found on the cflib.org site:
<cfset myArray = application.ADF.data.queryToArrayOfStructures(myQuery)>
- Connect two CommonSpot elements together using the new General Chooser and Custom Element Select custom field types
- Download applications built using the ADF and add features to your site like Profiles, Forums, Blogs
- Build Applications using the ADF to distribute amongst your CommonSpot sites or share with the Community
- Add lightbox interfaces to any of your applications/custom field types using code like:
<cfset application.ADF.scripts.loadADFLightbox()> <div rel="myCustomScript.cfm" class="ADFLightbox">Open in lightbox</div>
Body of the myCustomScript.cfm file being opened in the lightbox
<cfset application.ADF.scripts.loadADFLightbox()>
<cfset application.ADF.ui.lightboxHeader(lbTitle="myCustomScript")>
<cfoutput>{Lightbox Page Content}</cfoutput>
<cfset application.ADF.ui.lightboxFooter()>
Getting Started
The best way to get started using the ADF is to Install it. Once you have the ADF installed you can:
- Browse the applications available on the Community Site